Welcome to the world of neonatal resuscitation with the epi dose NRP 8th edition! This essential guide equips healthcare professionals with the latest knowledge and techniques to ensure the best possible outcomes for newborns in critical situations.
The NRP 8th edition has undergone significant revisions, incorporating the latest evidence-based practices and research findings. Join us as we delve into the depths of this updated edition, exploring the key changes, algorithms, medications, and special considerations that shape the landscape of neonatal resuscitation.
Overview of NRP 8th Edition
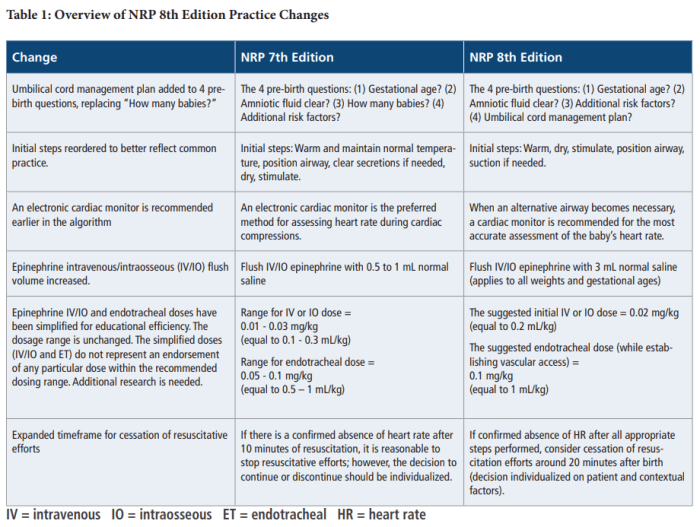
The Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP) is a set of evidence-based guidelines for the resuscitation of newborns. The 8th edition of the NRP was published in 2021 and represents the most up-to-date recommendations for neonatal resuscitation.
The NRP was first developed in 1987 and has been revised every few years to reflect new research and evidence. The 8th edition of the NRP includes several key changes and updates, including:
- New guidelines for the use of chest compressions in newborns
- Updated recommendations for the use of oxygen and ventilation
- New algorithms for the management of meconium aspiration syndrome and neonatal seizures
These changes and updates are based on the latest research and evidence and are designed to improve the outcomes of newborns who require resuscitation.
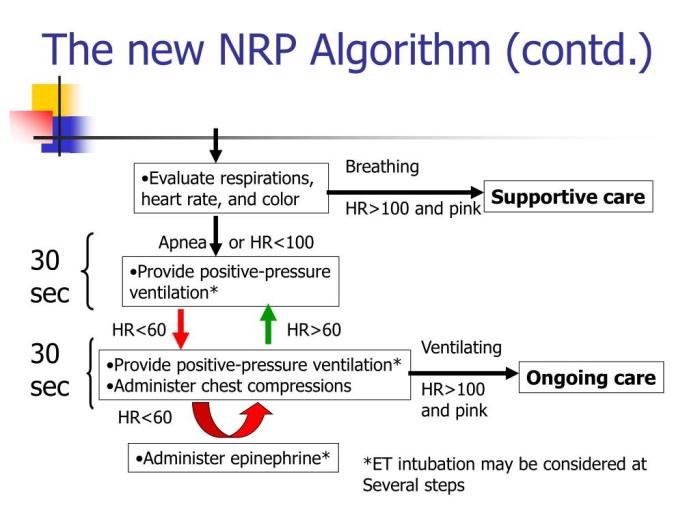
Resuscitation Algorithms
The NRP 8th edition provides structured algorithms to guide healthcare providers through various resuscitation scenarios. These algorithms prioritize rapid recognition of the patient’s condition and initiate appropriate interventions based on evidence-based practices.
Organization of Resuscitation Algorithms
The NRP 8th edition organizes the resuscitation algorithms into a comprehensive table with four columns:
| Algorithm | Indication | Steps | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Life Support (BLS) | Unresponsive and not breathing |
|
|
| Advanced Life Support (ALS) | Unresponsive, not breathing, or no pulse |
|
|
| Post-Resuscitation Care | After successful resuscitation |
|
|
Each algorithm provides a step-by-step guide for healthcare providers to follow during a resuscitation event. The steps are evidence-based and designed to optimize patient outcomes.
The eighth edition of the NRP (National Registry of Paramedics) Epi Dose Calculator is a valuable tool for healthcare professionals. It provides quick and accurate medication dosing information for various patient populations. Whether you’re preparing for the AP Government Unit 1 FRQ or managing critical care situations, the Epi Dose NRP 8th edition remains an indispensable resource for ensuring optimal patient outcomes.
Medications and Doses
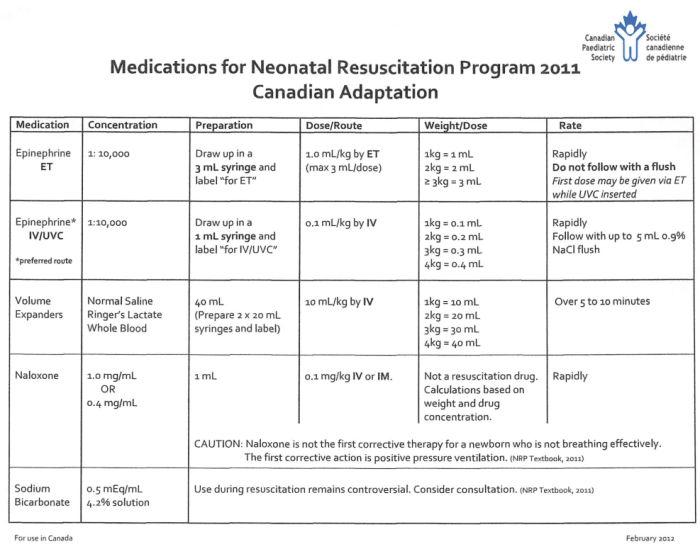
Medications play a crucial role in neonatal resuscitation, providing immediate support and intervention to stabilize and improve the health of newborns. NRP 8th edition provides updated guidelines for the administration of medications during resuscitation, ensuring the safe and effective use of these life-saving drugs.
The following table summarizes the key medications and doses used in NRP 8th edition, along with their indications, routes of administration, and special considerations:
Medication Summary Table
| Medication | Indication | Dose | Route of Administration | Special Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epinephrine | Cardiac arrest or pulseless bradycardia | 0.01-0.03 mg/kg | Endotracheal tube or intravenous | May cause arrhythmias, hypertension |
| Sodium Bicarbonate | Severe metabolic acidosis (pH < 7.0) | 1-2 mEq/kg | Intravenous | Can cause hypernatremia, alkalosis |
| Glucose | Hypoglycemia | 2 ml/kg of D10W | Intravenous | Can cause hyperglycemia |
| Calcium Chloride | Hypocalcemia | 0.5-1.0 mEq/kg | Intravenous | Can cause hypercalcemia, bradycardia |
| Magnesium Sulfate | Neonatal seizures | 20-40 mg/kg | Intravenous | Can cause respiratory depression, hypotension |
| Naloxone | Opioid overdose | 0.01-0.02 mg/kg | Intravenous or intramuscular | Can cause withdrawal symptoms |
It’s important to note that the indications, contraindications, and potential side effects of each medication should be carefully considered before administration. Healthcare providers should have a thorough understanding of the pharmacology and potential risks associated with these medications to ensure their safe and effective use in neonatal resuscitation.
Special Considerations
Resuscitation in different patient populations, such as neonates, infants, and children, requires special considerations due to their unique physiological and developmental characteristics.
The NRP 8th edition provides specific guidelines and modifications for resuscitation in these populations to ensure optimal outcomes.
Neonates
- Smaller airway and higher respiratory rate
- Thinner skin and greater heat loss
- Immature immune system
NRP 8th edition recommends:
- Smaller resuscitation equipment and lower ventilation rates
- Warming devices and thermal protection
- Early administration of antibiotics
Infants, Epi dose nrp 8th edition
- Larger airway and lower respiratory rate compared to neonates
- Still have immature immune system
- Greater head circumference relative to body size
NRP 8th edition recommends:
- Appropriate resuscitation equipment and ventilation rates
- Continued use of warming devices and thermal protection
- Close monitoring for signs of infection
Children
- Adult-sized airway and respiratory rate
- Fully developed immune system
- Greater body mass and height
NRP 8th edition recommends:
- Use of adult resuscitation equipment and techniques
- Focus on airway management and ventilation
- Consideration of underlying medical conditions
Education and Training: Epi Dose Nrp 8th Edition

Education and training are crucial for effective implementation of NRP guidelines. Healthcare professionals at all levels should receive appropriate training to ensure they possess the knowledge and skills to provide high-quality resuscitation care.
Levels of NRP Certification
NRP offers different levels of certification to cater to varying roles and responsibilities of healthcare providers. These levels include:
-
-*NRP Provider
This is the basic level of certification designed for healthcare professionals who are directly involved in resuscitation efforts.
-*NRP Instructor
This level is intended for individuals who are responsible for training and educating others in NRP.
-*NRP Course Director
This advanced level is designed for those who oversee NRP training programs and ensure their quality.
Each level has specific requirements for certification, including attendance at approved courses, passing written and practical examinations, and maintaining continuing education credits.
NRP Education and Training Resources
The American Heart Association (AHA) and other accredited organizations offer NRP education and training programs. These programs provide comprehensive training materials, hands-on practice sessions, and opportunities for skill evaluation.Healthcare professionals are encouraged to seek NRP certification and attend refresher courses regularly to stay updated on the latest resuscitation guidelines and techniques.
Quick FAQs
What are the key changes in the NRP 8th edition?
The NRP 8th edition incorporates several key changes, including revised resuscitation algorithms, updated medication dosages, and a focus on team-based resuscitation.
What are the indications for epinephrine administration in neonates?
Epinephrine is indicated for neonates with persistent bradycardia or asystole after initial resuscitation efforts.
How is the dose of epinephrine calculated for neonates?
The dose of epinephrine for neonates is 0.01 mg/kg, administered intravenously or intraosseously.