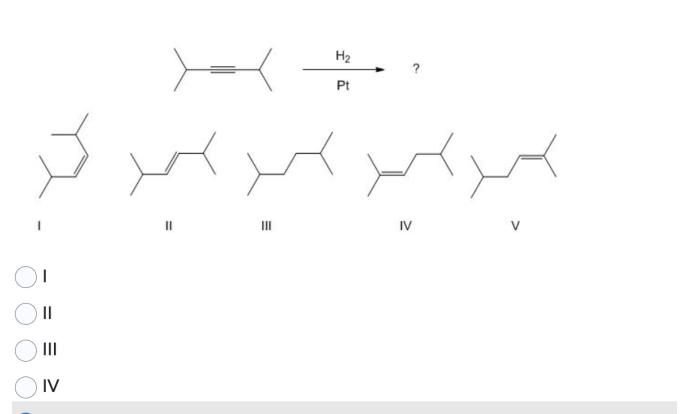
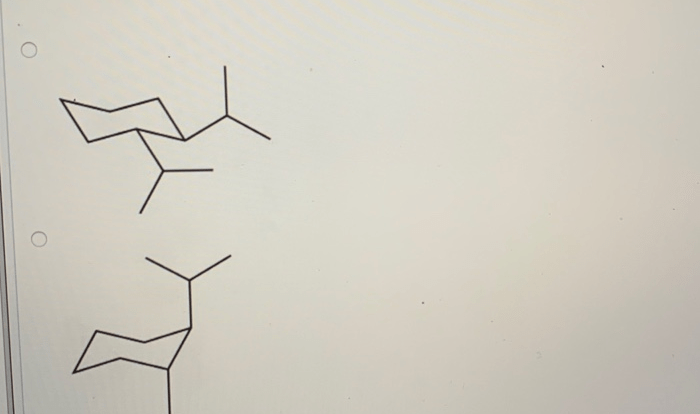
Organic chemistry reactions for mcat – Organic chemistry reactions play a pivotal role in the MCAT, demanding a comprehensive understanding for success. This guide delves into the intricacies of these reactions, equipping you with a solid foundation to excel in this challenging subject.
Delve into the types, mechanisms, and stereochemistry of organic chemistry reactions, gaining insights into their applications and experimental techniques. Safety considerations are also addressed, ensuring a well-rounded understanding for effective MCAT preparation.
Types of Organic Chemistry Reactions
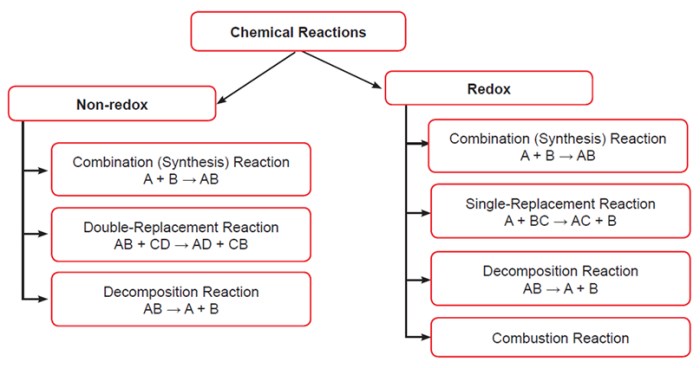
Organic chemistry reactions involve changes in the molecular structure of organic compounds. These reactions can be classified into four main types: addition, elimination, substitution, and rearrangement.
Addition Reactions
In addition reactions, two or more molecules combine to form a single product. These reactions typically involve the addition of an electrophile (electron-loving species) to a nucleophile (electron-donating species).
- Example:The addition of hydrogen to an alkene to form an alkane.
Elimination Reactions
In elimination reactions, a single molecule loses two or more atoms or groups of atoms to form a smaller product. These reactions typically involve the removal of a leaving group (a group that can easily depart with its electrons) from a substrate.
- Example:The elimination of water from an alcohol to form an alkene.
Substitution Reactions
In substitution reactions, one atom or group of atoms in a molecule is replaced by another atom or group of atoms. These reactions typically involve the attack of a nucleophile on an electrophile.
- Example:The substitution of a chlorine atom in an alkyl halide with a hydroxyl group to form an alcohol.
Rearrangement Reactions, Organic chemistry reactions for mcat
In rearrangement reactions, the atoms in a molecule are rearranged to form a new molecule with a different structure. These reactions typically involve the movement of a functional group from one atom to another.
- Example:The rearrangement of a carbocation to form a more stable carbocation.
Mechanisms of Organic Chemistry Reactions
Organic chemistry reactions proceed through specific mechanisms that involve the breaking and formation of chemical bonds. These mechanisms are categorized based on the nature of the attacking species and the reaction intermediate formed.
Nucleophilic Attack
In nucleophilic attack, a nucleophile (an electron-rich species) attacks an electrophile (an electron-deficient species) and forms a new bond. The nucleophile donates a pair of electrons to the electrophile, resulting in the formation of a new covalent bond.
Steps involved in nucleophilic attack:
- Formation of a nucleophile-electrophile complex
- Attack of the nucleophile on the electrophile
- Formation of a new covalent bond and breaking of the old bond
- Departure of the leaving group
Electrophilic Attack
In electrophilic attack, an electrophile (an electron-deficient species) attacks a nucleophile (an electron-rich species) and forms a new bond. The electrophile accepts a pair of electrons from the nucleophile, resulting in the formation of a new covalent bond.
Steps involved in electrophilic attack:
- Formation of an electrophile-nucleophile complex
- Attack of the electrophile on the nucleophile
- Formation of a new covalent bond and breaking of the old bond
- Departure of the leaving group
Free Radical Reactions
Free radical reactions involve the formation of free radicals, which are highly reactive species with unpaired electrons. Free radicals can be formed through homolytic bond cleavage, where a covalent bond breaks, and each atom takes one of the electrons.
Steps involved in free radical reactions:
- Initiation: Formation of free radicals
- Propagation: Reaction of free radicals with other molecules to form new free radicals
- Termination: Reaction of free radicals with each other to form stable products
Stereochemistry of Organic Chemistry Reactions

Stereochemistry plays a crucial role in organic chemistry, as it deals with the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms and groups within molecules. Understanding stereochemistry is essential for comprehending the outcome and mechanisms of organic reactions.
Enantiomersand diastereomersare two key concepts in stereochemistry. Enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images of each other, while diastereomers are non-superimposable stereoisomers that are not mirror images. The presence of chiral centers in a molecule can give rise to enantiomers, while the presence of multiple stereocenters can lead to diastereomers.
Regioselectivity and Stereoselectivity
Regioselectivityrefers to the preferential formation of one product over another based on the position of the functional group or reactive site. In contrast, stereoselectivityinvolves the preferential formation of one stereoisomer over another. Stereoselective reactions can be further classified as enantioselective or diastereoselective, depending on whether enantiomers or diastereomers are formed preferentially.
Stereochemistry significantly impacts the outcome of organic reactions. It can affect the reactivity of molecules, the reaction pathways, and the stereochemical outcome of the products. Understanding stereochemistry is crucial for predicting the products of organic reactions and designing synthetic strategies for target molecules.
Applications of Organic Chemistry Reactions
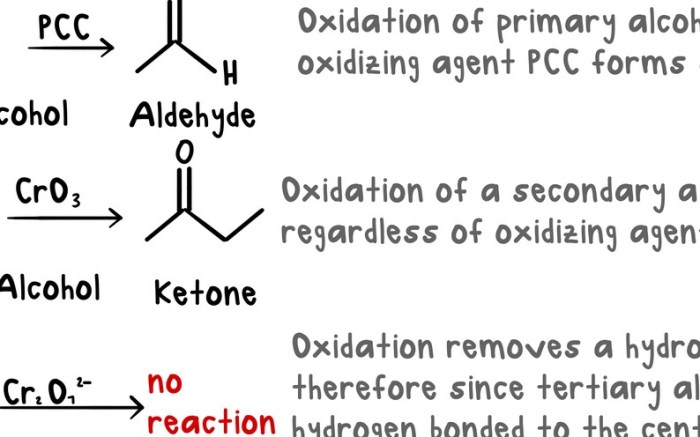
Organic chemistry reactions play a pivotal role in numerous fields, driving advancements in pharmaceuticals, materials science, agriculture, and beyond. These reactions enable the synthesis of complex molecules with specific properties, leading to the development of innovative products and solutions.
Pharmaceuticals
In the pharmaceutical industry, organic chemistry reactions are indispensable for the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). These reactions allow chemists to create drugs with precise molecular structures and functionalities, targeting specific diseases and improving patient outcomes. For example, the blockbuster drug Lipitor, used to lower cholesterol, is synthesized through a series of organic reactions involving alkylation, oxidation, and cyclization.
Materials Science
Organic chemistry reactions are essential for the development of advanced materials with tailored properties. These reactions enable the creation of polymers, plastics, and composites with enhanced strength, durability, and functionality. For instance, Kevlar, a lightweight and incredibly strong material used in bulletproof vests, is synthesized through the polymerization of terephthalic acid and p-phenylenediamine.
Agriculture
In agriculture, organic chemistry reactions contribute to the development of fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides. These reactions allow chemists to design molecules that enhance crop yield and protect plants from pests and diseases. For example, the herbicide glyphosate, commonly known as Roundup, is synthesized through a series of organic reactions involving acylation and alkylation.
Experimental Techniques in Organic Chemistry
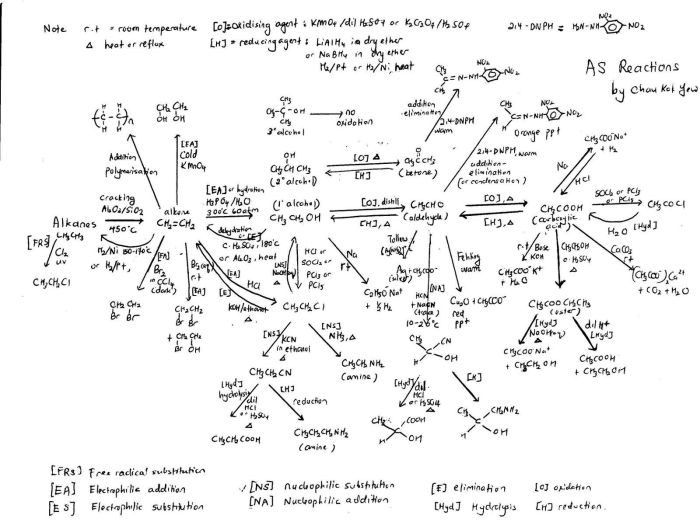
Organic chemistry involves a wide range of experimental techniques used to synthesize, purify, and characterize organic compounds. These techniques are essential for studying the properties and reactivity of organic molecules and for developing new synthetic methods.
Synthesis
Organic synthesis is the process of creating new organic compounds from simpler starting materials. There are many different types of synthetic reactions, each with its own unique set of conditions and reagents. Common synthetic techniques include:
- Nucleophilic substitution
- Electrophilic addition
- Elimination reactions
- Condensation reactions
- Pericyclic reactions
Purification
Once an organic compound has been synthesized, it is often necessary to purify it to remove impurities. Purification techniques include:
- Distillation
- Crystallization
- Chromatography
- Recrystallization
- Sublimation
Characterization
Characterization techniques are used to identify and determine the structure of organic compounds. These techniques include:
- Spectroscopy (NMR, IR, UV-Vis)
- Mass spectrometry
- Elemental analysis
- X-ray crystallography
Safety Considerations in Organic Chemistry: Organic Chemistry Reactions For Mcat
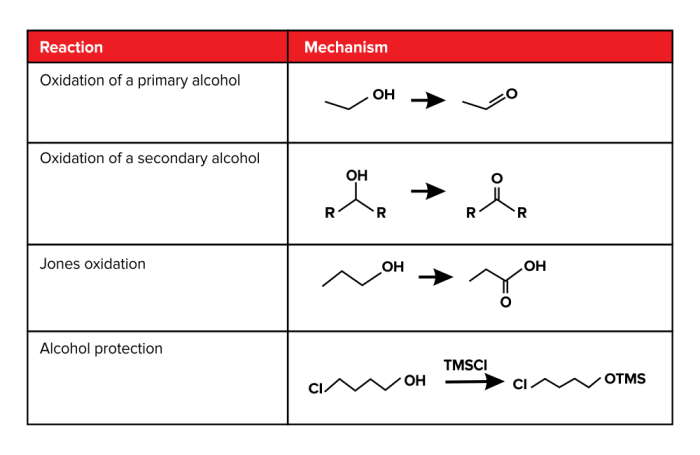
Organic chemistry involves working with hazardous chemicals, which necessitates adherence to strict safety guidelines to minimize risks and ensure a safe laboratory environment.
Proper handling of chemicals, waste disposal, and adherence to laboratory protocols are crucial for the safety of individuals and the prevention of accidents.
Guidelines for Safe Laboratory Practices
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, lab coats, and safety goggles at all times.
- Handle flammable solvents with care, keep them away from heat sources, and use them in well-ventilated areas.
- Never mix chemicals unless instructed to do so, and always add acid to water, not vice versa.
- Dispose of chemical waste properly according to established protocols, and never pour chemicals down the drain.
- Be aware of the potential hazards of each chemical used and take necessary precautions.
- Report any accidents or spills immediately and follow emergency procedures.
- Maintain a clean and organized laboratory workspace to minimize the risk of accidents.
FAQ Guide
What are the major types of organic chemistry reactions?
Addition, elimination, substitution, and rearrangement reactions.
How do nucleophilic attacks occur in organic chemistry reactions?
Nucleophiles attack electrophilic centers, forming new bonds and breaking old ones.
What is the significance of stereochemistry in organic chemistry reactions?
Stereochemistry determines the spatial arrangement of atoms, affecting the reactivity and properties of molecules.