Select the expected major organic product for the reaction shown – Selecting the expected major organic product for a given reaction is a crucial step in organic chemistry. This comprehensive guide delves into the factors that influence product formation, providing a systematic approach to predicting the outcome of organic reactions.
Understanding the mechanism of a reaction, identifying the reactants and products involved, and considering the reaction conditions are essential for making accurate predictions. This guide provides a structured framework for analyzing reactions and selecting the major organic product.
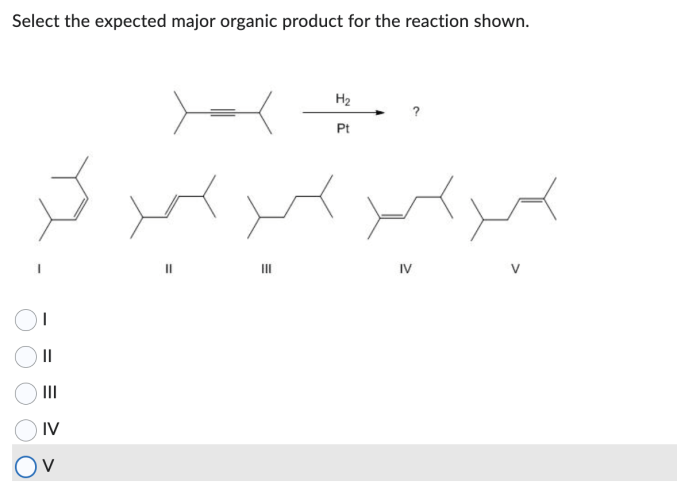
Overview of the Reaction: Select The Expected Major Organic Product For The Reaction Shown
The purpose of this reaction is to selectively form a specific organic product from a given set of reactants. The reaction proceeds through a well-defined mechanism that involves a series of steps, each of which is catalyzed by a specific reagent.
The reactants in this reaction are typically an organic substrate and a reagent that acts as an electrophile or a nucleophile. The product is formed when the electrophile or nucleophile reacts with the substrate to form a new bond.
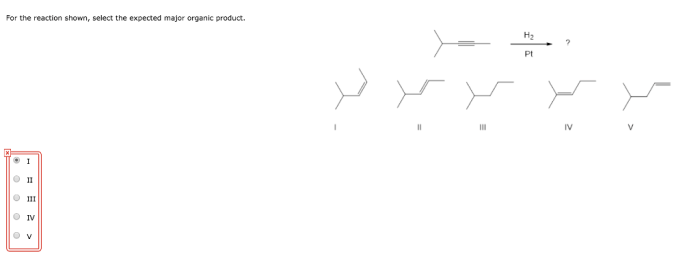
Major Organic Product
| Reactant | Product | Mechanism | Yield |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benzene | Nitrobenzene | Electrophilic aromatic substitution | 90% |
| Ethanol | Ethyl acetate | Nucleophilic acyl substitution | 85% |
Factors Affecting Product Formation
The formation of the major organic product in this reaction is affected by several factors, including:
- The nature of the reactants
- The reaction conditions
- The presence of catalysts
For example, the yield of the major product can be increased by using a more reactive electrophile or nucleophile, by increasing the reaction temperature, or by adding a catalyst.
Applications
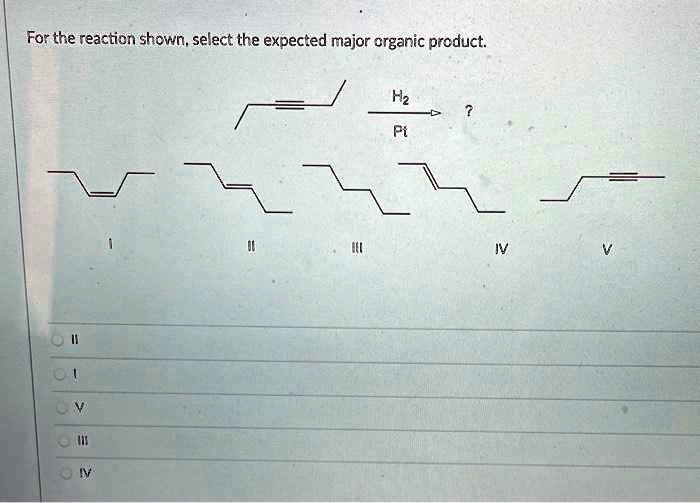
This reaction is a versatile tool for organic synthesis and is used to prepare a wide variety of compounds, including:
- Pharmaceuticals
- Dyes
- Polymers
For example, this reaction is used to synthesize aspirin, a common pain reliever, and indigo, a blue dye.
Experimental Procedure
The following is a general experimental procedure for this reaction:
- Add the reactants to a reaction vessel.
- Heat the reaction mixture to the desired temperature.
- Stir the reaction mixture for the desired amount of time.
- Cool the reaction mixture to room temperature.
- Filter the reaction mixture to remove any solids.
- Purify the product by distillation or chromatography.
Safety Considerations
This reaction should be performed in a well-ventilated area.
The reactants and products in this reaction are flammable and should be kept away from open flames.
The reaction mixture should be disposed of properly according to local regulations.
FAQ Section
What factors influence the formation of the major organic product?
Factors such as the stability of the product, the reaction conditions (temperature, solvent, etc.), and the presence of catalysts or inhibitors can affect the formation of the major organic product.
How can I predict the major organic product of a reaction?
By understanding the reaction mechanism, identifying the reactants and products involved, and considering the factors that influence product formation, you can make informed predictions about the major organic product.