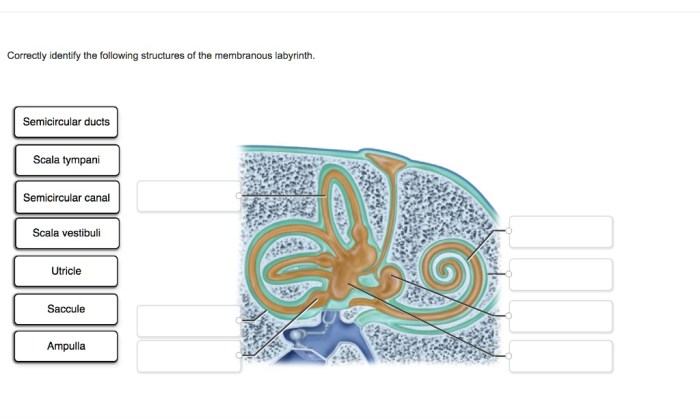
Correctly identify the following structures of the membranous labyrinth – The membranous labyrinth, a crucial component of the inner ear, plays a vital role in hearing and balance. Understanding its structures is essential for comprehending these sensory functions. This discussion aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the cochlea, vestibular system, semicircular canals, utricle and saccule, and endolymph and perilymph, enabling a thorough grasp of their anatomy and significance.
Cochlea
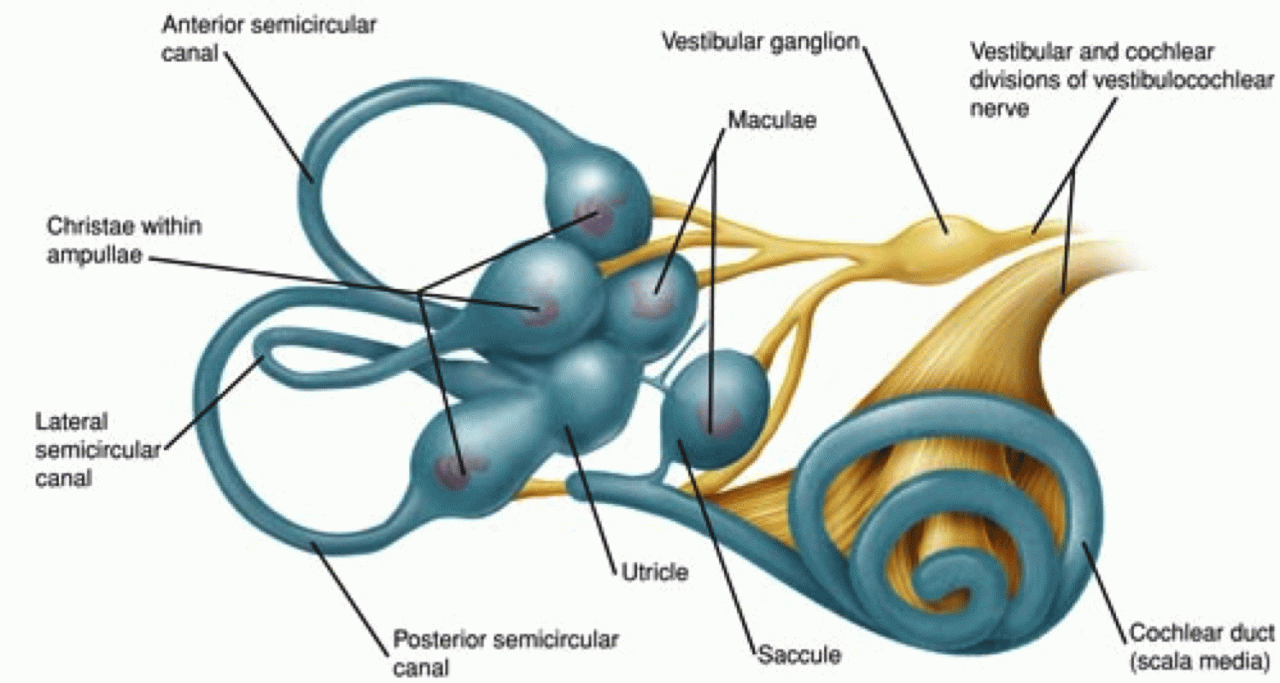
The cochlea is a spiral-shaped organ located in the inner ear. It is responsible for converting sound waves into electrical signals that are then sent to the brain. The cochlea is filled with fluid and contains a basilar membrane that is lined with hair cells.
When sound waves enter the cochlea, they cause the basilar membrane to vibrate. This vibration stimulates the hair cells, which then send electrical signals to the brain.The cochlea is divided into three sections: the scala vestibuli, the scala tympani, and the scala media.
The scala vestibuli is located on the outside of the cochlea and contains perilymph, a fluid that is similar to cerebrospinal fluid. The scala tympani is located on the inside of the cochlea and also contains perilymph. The scala media is located between the scala vestibuli and the scala tympani and contains endolymph, a fluid that is high in potassium and low in sodium.The
hair cells in the cochlea are arranged in four rows, with each row responding to a different frequency of sound. The highest frequencies are detected by the hair cells in the outer row, while the lowest frequencies are detected by the hair cells in the inner row.The
cochlea is a vital organ for hearing. It allows us to perceive sound and to determine the direction from which sound is coming.
Vestibular System
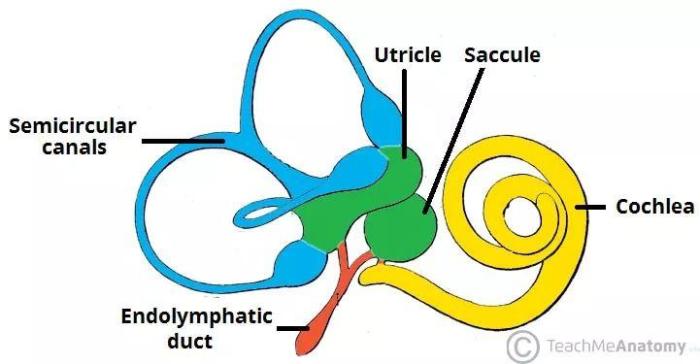
The vestibular system is a complex network of organs located in the inner ear that is responsible for balance and spatial orientation. It consists of the semicircular canals, the utricle, and the saccule.The semicircular canals are three fluid-filled tubes that are arranged in three planes: the horizontal plane, the frontal plane, and the sagittal plane.
When the head moves, the fluid in the semicircular canals moves, which stimulates the hair cells in the canals. These hair cells then send signals to the brain, which interprets the movement of the head and adjusts the body’s position accordingly.The
utricle and the saccule are two small sacs that are located in the inner ear. They contain hair cells that are embedded in a gelatinous substance. When the head tilts, the gelatinous substance moves, which stimulates the hair cells. These hair cells then send signals to the brain, which interprets the tilt of the head and adjusts the body’s position accordingly.The
vestibular system is a vital organ for balance and spatial orientation. It allows us to maintain our balance, even when we are moving, and to determine our orientation in space.
Semicircular Canals

The semicircular canals are three fluid-filled tubes that are arranged in three planes: the horizontal plane, the frontal plane, and the sagittal plane. They are part of the vestibular system, which is responsible for balance and spatial orientation.When the head moves, the fluid in the semicircular canals moves, which stimulates the hair cells in the canals.
These hair cells then send signals to the brain, which interprets the movement of the head and adjusts the body’s position accordingly.The horizontal semicircular canal is responsible for detecting movement in the horizontal plane. The frontal semicircular canal is responsible for detecting movement in the frontal plane.
The sagittal semicircular canal is responsible for detecting movement in the sagittal plane.The semicircular canals are essential for maintaining balance. They allow us to keep our balance, even when we are moving, and to determine our orientation in space.
Utricle and Saccule
The utricle and the saccule are two small sacs that are located in the inner ear. They are part of the vestibular system, which is responsible for balance and spatial orientation.The utricle is responsible for detecting linear acceleration in the horizontal plane.
The saccule is responsible for detecting linear acceleration in the vertical plane.The utricle and the saccule contain hair cells that are embedded in a gelatinous substance. When the head moves, the gelatinous substance moves, which stimulates the hair cells. These hair cells then send signals to the brain, which interprets the movement of the head and adjusts the body’s position accordingly.The
utricle and the saccule are essential for maintaining balance. They allow us to keep our balance, even when we are moving, and to determine our orientation in space.
Endolymph and Perilymph
The endolymph and the perilymph are two fluids that are found in the inner ear. The endolymph is a high-potassium, low-sodium fluid that fills the scala media, which is located between the scala vestibuli and the scala tympani. The perilymph is a low-potassium, high-sodium fluid that fills the scala vestibuli and the scala tympani.The
endolymph and the perilymph play an important role in the function of the inner ear. The endolymph is essential for the proper functioning of the hair cells in the cochlea and the vestibular system. The perilymph provides a stable environment for the hair cells and helps to protect them from damage.The
endolymph and the perilymph are essential for hearing and balance. They allow us to hear sounds and to maintain our balance, even when we are moving.
Q&A: Correctly Identify The Following Structures Of The Membranous Labyrinth
What is the function of the cochlea?
The cochlea is responsible for converting sound waves into neural signals, enabling us to perceive sound.
How do the semicircular canals contribute to balance?
The semicircular canals detect rotational movements of the head, providing information crucial for maintaining equilibrium.
What is the difference between endolymph and perilymph?
Endolymph is found within the membranous labyrinth, while perilymph fills the space between the membranous and bony labyrinths. Endolymph has a high potassium ion concentration, while perilymph has a high sodium ion concentration.